Mutual TLS¶
When performing mutual TLS (or mTLS for short), trust must be established in both directions. We’ve already discussed how a client trusts a server, here we’ll also cover how a server can trust a client.
As in other sections, the certificates in Appendix will be used
here. The server will continue to use the set of certificates signed by
docs/tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem while the client will use the set of
certificates signed by docs/alternate-tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem. This avoids
any issues where a client is trusted by accident by sharing a CA with the
server.
Node.js Server¶
The example mTLS server is very similar to the original TLS server. The primary
differences are usage of the requestCert and rejectUnauthorized TLS
options and adding the ability to add an extra CA to use when trusting the
client certificate:
const options = {
key: fs.readFileSync(cliOptions.key),
cert: fs.readFileSync(cliOptions.cert),
requestCert: true,
rejectUnauthorized: false,
}
if (cliOptions.rootCA) {
options.ca = [fs.readFileSync(cliOptions.rootCA)]
}
as well as a listener added for secureConnection events that can be used to
provide an error reason in cases where mTLS is not successful:
server.on('secureConnection', secureConnectionCallback)
Without Extra Root CA¶
By running the server without an extra CA, it’s in a similar state as the TLS server:
cd docs/nodejs/
node server-mtls.js \
--cert ../tls-certs/localhost-server-cert.pem \
--key ../tls-certs/localhost-server-key.pem
# Example mTLS app listening at https://localhost:9443
Making a request with curl that doesn’t specify any client certificate
information still results in a validation error:
$ curl --cacert ../tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem https://localhost:9443
{"mTLSValid": false, "reason": "UNABLE_TO_GET_ISSUER_CERT"}
This is because curl has seen a “Certificate Request” TSLv1.2 record
layer from the Node.js server (due to requestCert: true) and in turn
curl presented a “Certificate” record layer containing a list of 0
certificates:
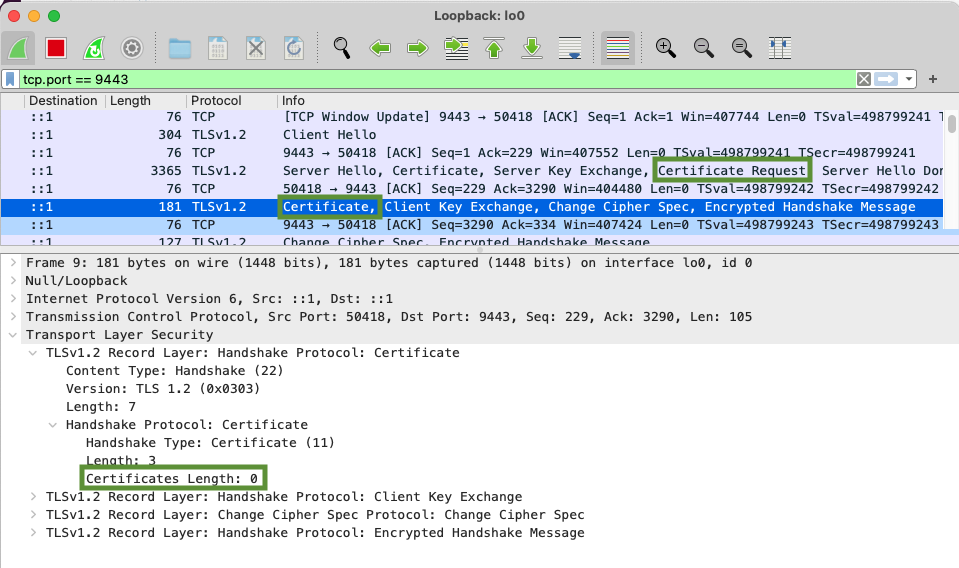
If we decide to actually present a client certificate, the server fails to validate with a similar error, because the client’s CA is not known to the server:
$ curl \
> --cacert ../tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem \
> --key ../alternate-tls-certs/localhost-client-key.pem \
> --cert ../alternate-tls-certs/localhost-client-chain.pem \
> https://localhost:9443
{"mTLSValid": false, "reason": "UNABLE_TO_GET_ISSUER_CERT_LOCALLY"}
With Extra Root CA¶
By running the server with the client’s CA added:
cd docs/nodejs/
node server-mtls.js \
--cert ../tls-certs/localhost-server-cert.pem \
--key ../tls-certs/localhost-server-key.pem \
--root-ca ../alternate-tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem
# Example mTLS app listening at https://localhost:9443
after which the curl request passes validation
$ curl \
> --cacert ../tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem \
> --key ../alternate-tls-certs/localhost-client-key.pem \
> --cert ../alternate-tls-certs/localhost-client-chain.pem \
> https://localhost:9443
{"mTLSValid": true}
Node.js Client¶
There isn’t much difference in making a request with axios that uses mTLS
instead of one-way TLS. The primary difference here is the use of the
client private key and public certificate:
const options = {}
options.cert = fs.readFileSync(cliOptions.cert)
options.key = fs.readFileSync(cliOptions.key)
if (cliOptions.rootCA) {
options.ca = [fs.readFileSync(cliOptions.rootCA)]
}
const axiosOptions = {
httpsAgent: new https.Agent(options),
}
The requests below will hit server-mtls.js configured with
--root-ca ../alternate-tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem.
Using the one-way request.js, the server validation error is the same as
the one encountered by curl without a client certificate:
$ cd docs/nodejs/
$ node request.js \
> --root-ca ../tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem \
> --url https://localhost:9443
Response: {"mTLSValid":false,"reason":"UNABLE_TO_GET_ISSUER_CERT"}
By providing a --key and --cert in request-mtls.js, the request is valid:
$ cd docs/nodejs/
$ node request-mtls.js \
> --key ../alternate-tls-certs/localhost-client-key.pem \
> --cert ../alternate-tls-certs/localhost-client-chain.pem \
> --root-ca ../tls-certs/root-ca-cert.pem
{ mTLSValid: true }